Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a strategic process aimed at enhancing a website’s organic search visibility. It works by aligning your website’s content and structure with the ranking algorithms of search engines. These algorithms evaluate various factors, such as keyword usage, page speed, and backlinks, to determine how relevant your site is to a user’s query.
Google, as the most widely used search engine, continuously updates its algorithm using Natural Language Processing (NLP) models. These models, such as BERT and MUM, help the engine better understand the context of search queries. This means SEO isn’t only about keywords but also about how well your content matches user intent and search queries. By ensuring your content is semantically rich and contextually relevant, you increase your chances of ranking higher in search results.
How SEO Can Help You
SEO’s primary function is to improve organic search visibility, leading to increased traffic and, ultimately, business growth. Organic traffic is essential because it drives users to your site without the ongoing costs of paid advertising, such as Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns. SEO can provide long-term value if optimized properly.
Key Benefits:
- Increased Organic Traffic: SEO helps rank your website higher for relevant search terms, increasing the likelihood that users will find your site.
- Enhanced Credibility: Search engines favor websites with high-quality content and good user experiences. The higher you rank, the more users trust your website.
- Higher Return on Investment (ROI): Once your strategy is in place, you can continuously attract organic traffic without needing to spend on ads.
- User Experience Improvements: Many technical aspects of SEO, like mobile optimization and site speed, contribute to a better user experience, which in turn enhances your website’s performance in rankings.
Related article: How to Measure SEO Success.
The Basic Components of SEO
SEO is a complex system that involves multiple interconnected elements. To perform well, a website must meet various criteria, each contributing to its overall SEO health. Below is a detailed look at the main components:
Keyword Research
A vital first step in SEO is identifying the right keywords—terms your target audience searches for. Modern SEO emphasizes semantic keyword research, meaning the focus is on understanding the context behind search queries, not just individual keywords. For example, users searching for “best laptop 2024” are also interested in reviews, comparisons, and top features. Your content should cover all related topics comprehensively.
For deeper insights: Keyword Research.
Content Optimization
Content must not only be relevant but structured semantically. Google’s NLP models process how concepts are connected. Creating content that fully answers user queries, addresses subtopics, and uses clear, concise language enhances its relevance. Tools like Google’s BERT model analyze how well your content fits user intent, so writing for clarity and depth is critical.
Technical SEO
This aspect focuses on how search engines crawl and index your site. Websites with good technical SEO have clean site architecture, proper use of schema markup, optimized robots.txt, and sitemaps. Ensuring that search engines can efficiently understand and index your site is foundational to improving your rankings.
Learn more: Technical SEO.
On-Page SEO
Proper on-page SEO ensures that each page targets specific user intents. This includes:
- Optimizing title tags and meta descriptions to match search intent.
- Using header tags (H1, H2, etc.) for hierarchical clarity.
- Writing descriptive, semantically rich content that directly addresses the query.
Further reading: On-Page SEO.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO focuses on improving your site’s reputation by building backlinks from authoritative sites. Links from high-quality, relevant sites tell search engines that your website is a credible source of information. In addition, social signals and brand mentions also contribute to your website’s off-page SEO strength.
Related topic: Off-Page SEO.
How Search Engines Rank Content: An Overview
Search engines like Google use highly sophisticated algorithms that consider hundreds of ranking factors. To put it simply, they rank websites based on relevance and authority. Here’s how they work:
Crawling and Indexing
Search engines use bots (often called spiders) to crawl the web, discover content, and index it. Efficient crawling and a properly indexed site are essential for SEO success. Ensuring that your website is optimized for crawling through proper use of sitemaps, robots.txt, and canonical tags is a foundational part of technical SEO.
Ranking Algorithms
Search engines use NLP models, like Google’s RankBrain and BERT, to better understand and interpret user queries. These models assess how well a webpage answers the search query by looking at semantic relationships and user intent. For example, a page might not use the exact keyword the user searched for, but if it provides an authoritative answer, Google may still rank it highly.
More on this: How Google’s Ranking Algorithms Work.
User Experience (UX) Signals
Google also measures how users interact with your content—metrics like dwell time, bounce rate, and click-through rate (CTR) all impact rankings. SEO strategies that focus on user intent while delivering a seamless, engaging experience tend to perform better.
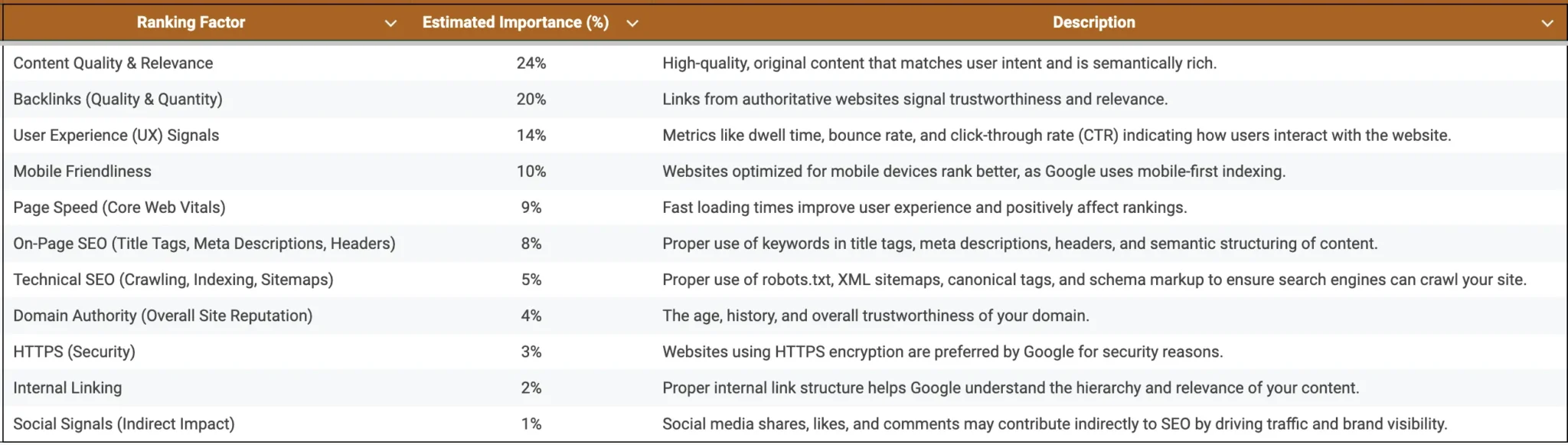
What Makes a Website SEO-Friendly?
A website is SEO-friendly when it is easy for both users and search engines to navigate. Here’s what defines an SEO-friendly site:
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means that the mobile version of your site is prioritized for ranking. Ensuring a responsive design that works well on mobile devices is critical.
- Fast Load Times: Page speed is a ranking factor. A slow website frustrates users and causes higher bounce rates, which signals poor quality to search engines. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to test and improve your site speed.
- Secure (HTTPS): A secure site with HTTPS encryption is a ranking factor. Security builds trust with users and search engines alike.
- Optimized Internal Links: An internal linking strategy helps search engines understand the structure of your website. Links between related content also boost user engagement by encouraging visitors to explore more of your site.
Learn more: Mobile SEO and Internal Linking.
Common SEO Terms Explained for Beginners
- SERP: Search Engine Results Page, the list of websites shown after a query.
- Crawling: Search engines scan and discover new pages.
- Indexing: Adding a page to a search engine’s database for retrieval.
- Backlinks: Links from external websites to your site, which act as votes of confidence.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of users who leave after viewing only one page, often indicating poor engagement.
The Role of Keywords in SEO
Keywords are search terms users type into search engines. SEO uses keywords strategically within content to signal relevance to search engines. Proper keyword research and placement are critical to improving search rankings. Tools like Google Keyword Planner help identify relevant keywords for your target audience.
Deep dive: Keyword Research.
SEO’s Relevance Across Different Industries
SEO is not a mere marketing trend—it is a strategic asset that has become fundamental to the success of businesses across virtually every industry. In the past two decades, as digital transformation has accelerated at a historic pace—with over 63% of the global population now online—SEO has become indispensable in navigating the complexities of the digital marketplace. E-commerce, financial services, healthcare, and education sectors, among others, rely heavily on SEO to maintain visibility and ensure long-term sustainability in their respective markets.
Take e-commerce, for example. With 53% of all web traffic being driven by organic search, SEO represents a direct and cost-efficient path to reaching consumers. Without a structured SEO approach, businesses in this sector are at risk of losing out on significant organic traffic—traffic that often translates into revenue. In industries like finance and healthcare, where trust, credibility, and accuracy are non-negotiable, SEO functions as a vital tool in positioning authoritative content, improving search rankings, and establishing the brand’s trustworthiness.
The Digital Growth of the Last 20 Years
The past two decades have seen an unprecedented shift toward digital platforms. Today, there are over 1.9 billion websites vying for attention. SEO has matured alongside this growth, evolving from rudimentary tactics to a sophisticated, data-driven approach aimed at delivering precise, intent-based content to users. Those companies that fail to embrace this evolution find themselves at a competitive disadvantage. Consider this: businesses that implement effective SEO strategies can see traffic growth of up to 300%, whereas those who ignore it are forced to compensate by spending 30-40% more on paid advertising just to remain visible.
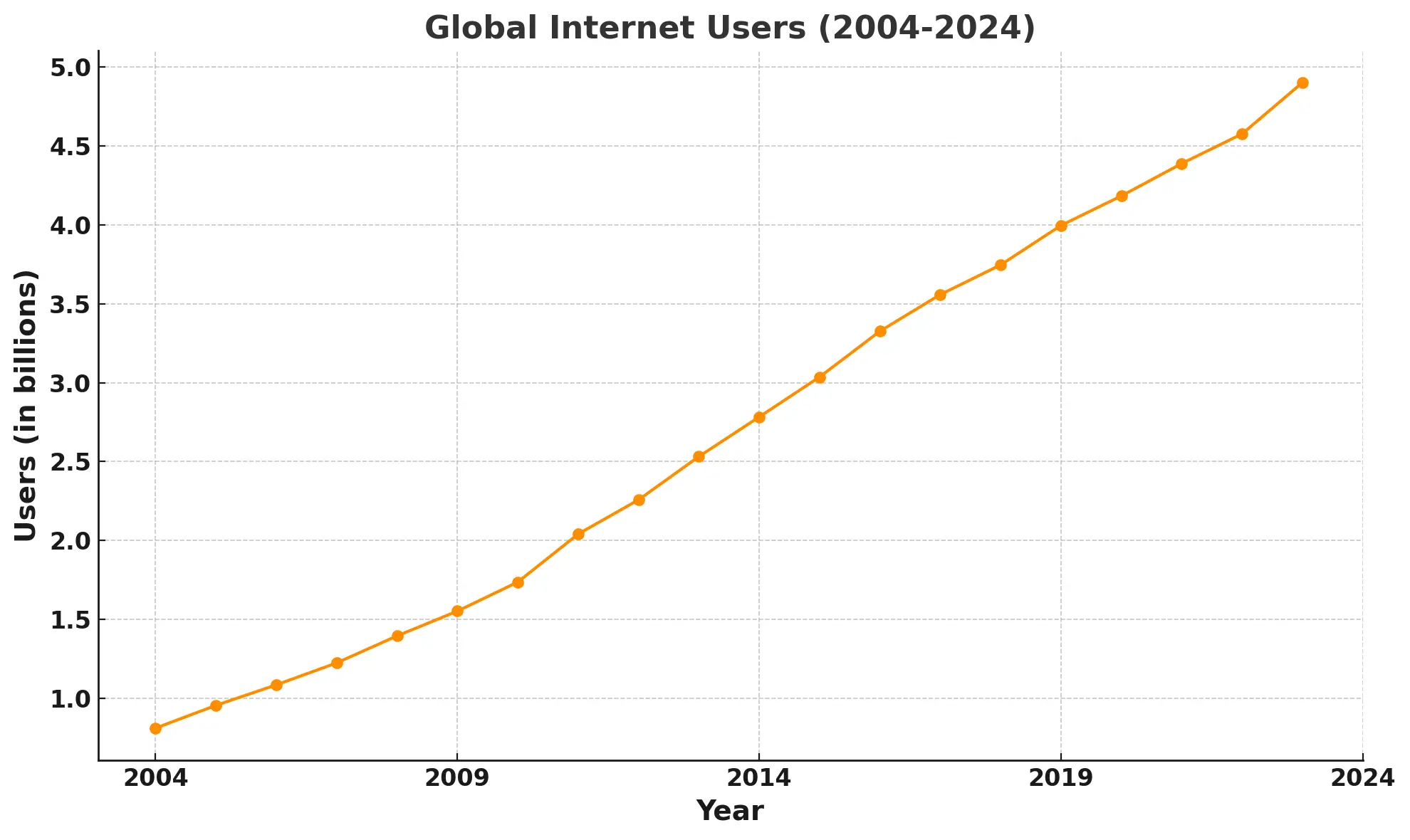
Moreover, the advent of mobile search and voice search, which now constitute nearly 60% of all global search activity, demands adaptation. SEO today must prioritize mobile responsiveness, page speed, and user experience—without which a company risks irrelevance in a marketplace that continues to shift toward mobile-first solutions.
Final Recommendations
SEO is not optional; it is essential. The data is clear: over 80% of users do not venture past the first page of search results. This reality places SEO at the forefront of any digital strategy. Without it, your business is effectively invisible to the vast majority of potential customers. Failure to optimize your website means forfeiting a significant competitive advantage and incurring unnecessary costs to maintain visibility through other means.
In our considered view, businesses that understand and invest in robust, forward-thinking SEO strategies not only enhance their online presence but also secure a competitive edge that is necessary to thrive in today’s digital economy. SEO offers an unparalleled opportunity for long-term, sustainable growth, increased customer acquisition, and heightened brand authority. The decision is simple: invest in SEO now or face the costly consequences of digital obscurity in the years ahead.
References:
- Google Search Central – SEO Starter Guide: Google provides detailed insights into best practices for SEO, covering everything from on-page to technical SEO.
- Moz – The Beginner’s Guide to SEO: Moz’s guide offers a comprehensive overview of SEO, explaining how search engines work and the key components of optimization.
- Ahrefs Blog – What is SEO?: Ahrefs offers a clear, step-by-step explanation of SEO basics, including keyword research, content optimization, and backlink strategies.
- Backlinko – SEO Basics: This source outlines essential SEO concepts, including why SEO is important, how search engines rank websites, and critical factors for success.
