Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has undergone significant changes since its inception in the 1990s. It evolved from basic keyword manipulation to a complex, data-driven strategy essential to digital marketing today. This detailed examination of SEO’s history explores key milestones and algorithm updates that shaped modern SEO practices.
Early Stages of SEO (1990s)
The 1990s marked the birth of SEO, coinciding with the rise of early search engines. This period was characterized by simple ranking factors, primarily keywords and meta tags.
Emergence of Search Engines
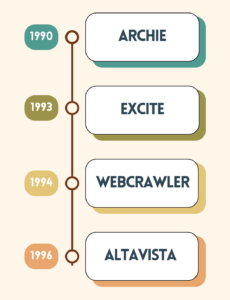
- 1990: Archie
Launched as the first search engine, Archie only indexed FTP archives and lacked full-text search capabilities. - 1993: Excite
Introduced relevance-based sorting, moving beyond simple keyword matching. - 1994: WebCrawler
First engine to index full-text web pages, making content within web pages searchable. - 1996: Altavista
Enhanced user experience with full-text search and an intuitive interface, setting the stage for mainstream adoption before Google’s dominance.
SEO Manipulation in the 1990s
Website owners quickly realized the importance of ranking higher, leading to early SEO tactics like:
- Keyword stuffing: Overloading pages with repetitive keywords.
- Meta tag manipulation: Over-relying on meta tags for ranking signals.
Keyword stuffing looks something like this:
Keyword stuffing is when keyword stuffing is used excessively in content to improve keyword stuffing rankings. Though keyword stuffing may seem effective, keyword stuffing actually harms readability and can lead to keyword stuffing penalties from keyword stuffing search engines.
Meta tag manipulation is something like this:
<meta name="description" content="Cheap hotels, affordable hotels, budget hotels, best hotel deals, discount hotels, hotel rooms, cheap hotel rates, budget-friendly hotels, low-cost hotels for vacation, affordable hotel booking, cheap hotel rates online, best cheap hotels available now.">These strategies worked in the early days but became obsolete as search engines advanced, pushing SEO toward more sophisticated methods.
Related article: For more on SEO tactics and their evolution, see our article on SEO Specializations.
Key Milestones in SEO Development
The 2000s saw significant developments driven by Google’s innovations. Algorithm updates shifted the focus from basic keyword tactics to ethical and complex SEO strategies.
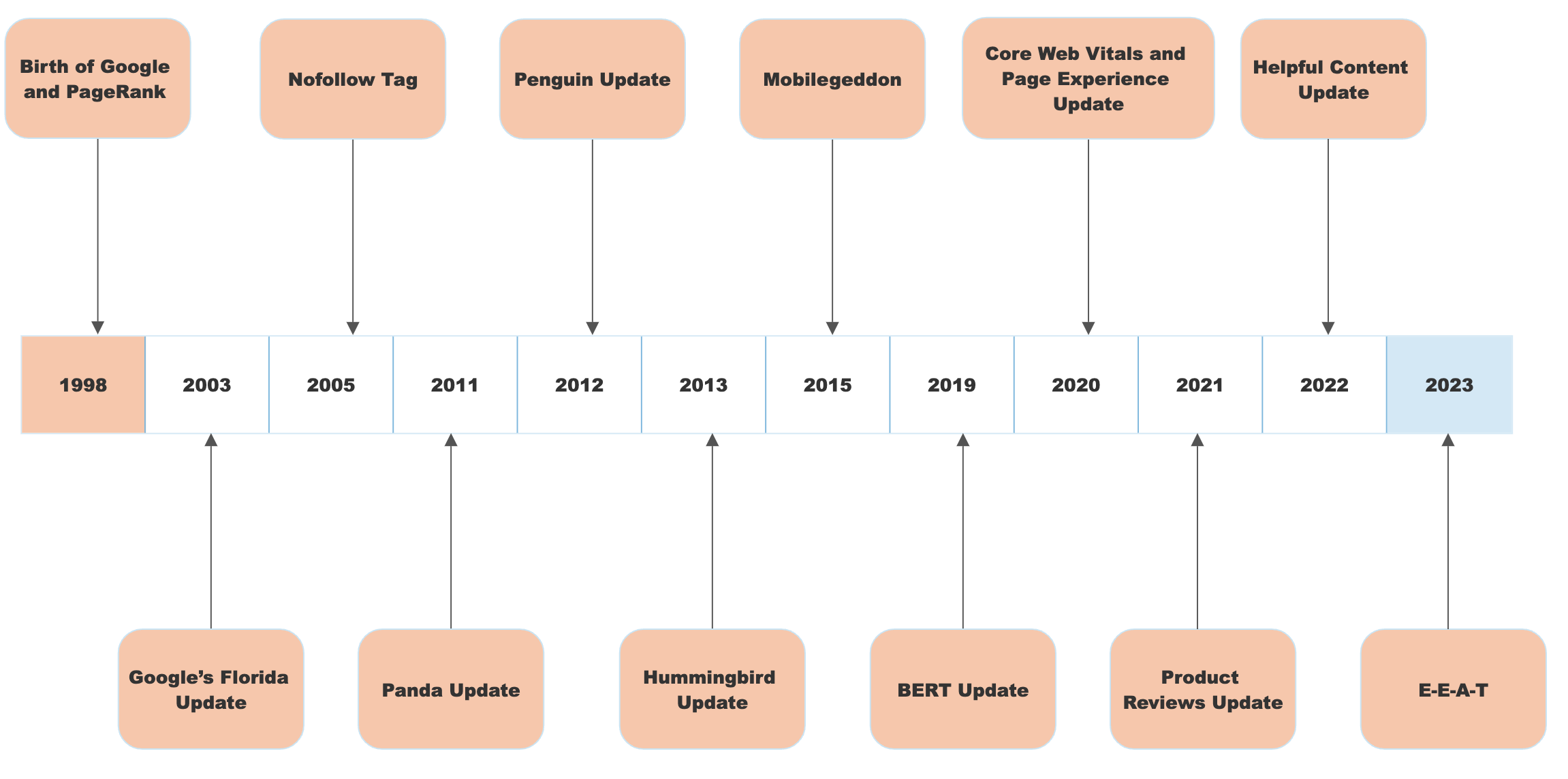
The Birth of Google and PageRank (1998)
Google’s introduction of the PageRank algorithm in 1998 revolutionized SEO by emphasizing backlinks:
- PageRank measured the quality and quantity of backlinks, prioritizing websites with more authoritative links.
- This marked the beginning of link-building as a key SEO strategy, with high-quality links leading to better rankings.
Learn more: See our Off-Page SEO subfolder for more on link-building strategies.
Rise of Ethical SEO (Early 2000s)
During the early 2000s, SEO transitioned from manipulative practices to ethical, content-focused strategies.
- 2003: Google’s Florida Update
Penalized keyword stuffing and manipulative tactics, pushing SEO toward white hat practices like valuable content creation and natural link-building. - 2005: Nofollow Tag
Introduced to combat spammy link practices, particularly in blog comments and paid links, by allowing webmasters to block certain links from passing PageRank.
Major Google Algorithm Updates
Google’s constant algorithm updates defined the evolution of SEO. Key updates include:
- 2011: Panda Update
Penalized websites with thin or low-quality content, prioritizing content-rich sites. - 2012: Penguin Update
Targeted sites using spammy backlinks, enforcing the need for high-quality link-building strategies. - 2013: Hummingbird Update
Introduced semantic search, helping Google understand the context of queries, shifting the focus from exact-match keywords to user intent. - 2015: Mobilegeddon
Prioritized mobile-friendly websites, making mobile optimization a critical ranking factor as mobile search surpassed desktop search. - 2019: BERT Update
Enhanced Google’s ability to understand natural language processing (NLP), focusing on user intent in complex and conversational queries.
Deep dive: For more details on Google’s updates, visit our subfolder on Google Algorithm Updates which dives deeper into all the updates on the google search engine algorithm has done so far.
Impact of Google Algorithm Updates on SEO
Panda (2011)
- Focused on improving content quality.
- Penalized sites with duplicate or thin content, pushing for more in-depth, valuable information.
Penguin (2012)
- Aimed at improving the quality of link profiles.
- Penalized sites with irrelevant or manipulative backlinks, such as those purchased or obtained through link farms.
Hummingbird (2013)
- A breakthrough in understanding search intent rather than relying on keyword matching.
- Made it essential for websites to address contextual user needs.
Mobilegeddon (2015)
- Pushed websites to become mobile-responsive and improve page loading times, reflecting the growth in mobile traffic.
BERT (2019)
- Focused on interpreting conversational queries, especially long-tail keywords.
- Further prioritized user intent, enabling better alignment between search results and the true meaning behind user queries.
Further reading: For more insights on how NLP impacts SEO, see our article on SEO and NLP.
SEO in Modern Digital Marketing
SEO’s role has expanded far beyond improving search rankings. It is now a key pillar of digital marketing, intertwined with content creation, user experience, and long-term growth strategies.
SEO as a Traffic Driver
SEO remains a primary source of organic traffic for websites. Unlike paid ads, SEO ensures sustained visibility, driving consistent traffic without ongoing costs.
Integration with Content Marketing
Content marketing and SEO work symbiotically:
- High-quality, optimized content helps websites rank higher.
- Content that aligns with user intent keeps visitors engaged, improving metrics like time on page and bounce rate, which indirectly influence rankings.
Explore more: See our Content Strategy for SEO subfolder for strategies on optimizing content for SEO.
User Experience (UX) and SEO
Google’s focus on user experience (UX) has brought aspects like:
- Page speed
- Mobile responsiveness
- Core Web Vitals
These factors are now essential for SEO, meaning sites must prioritize not just content but also technical performance.
Read more: Explore our Technical SEO subfolder for insights into how UX elements like page speed impact SEO.
Long-Term SEO Investment
SEO is a long-term strategy. While paid ads stop delivering traffic once budgets deplete, SEO can provide continuous organic traffic, yielding a better return on investment (ROI) over time.
Future of SEO
The history of SEO demonstrates that the landscape is ever-changing. Understanding its evolution helps marketers stay ahead of upcoming trends, ensuring they continue to drive organic growth in a competitive environment.
SEO has transformed from basic keyword manipulation into a sophisticated digital marketing strategy. By focusing on content quality, user experience, and link-building, modern SEO requires a holistic approach. Understanding its past ensures adaptability for future changes.
References:
- Search Engine Journal – History of SEO: This article traces the development of SEO from its early days to the present, including the major algorithm changes.
- Moz – A Brief History of Search Engines and SEO: Moz provides a detailed timeline of how search engines and SEO evolved, highlighting key moments in algorithm development.
- Google – How Search Works: Google offers insights into its algorithm and how it evaluates websites, providing context for major updates like Panda, Penguin, and BERT.
- Ahrefs Blog – Major Google Algorithm Updates: Ahrefs explains the most important Google algorithm updates like Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, and BERT, which transformed SEO practices.
